Sound - insulation Principle of Doors and Windows
When sound waves emitted by a sound source spread to other areas and have a noise impact on those areas, materials and structures that block the spread of sound waves are often set up along the path of the sound - wave propagation. As a result, the sound waves cannot penetrate these materials and structures smoothly, or a great deal of energy is lost when passing through these materials, so as to achieve the purpose of reducing the noise impact in the area that needs to be protected.
This noise - reduction method of setting a blocking structure on the sound - wave propagation path is called sound insulation.
Sound - wave Propagation Modes
According to the different sound - wave propagation modes, sound insulation is usually divided into two categories: one is airborne - sound insulation; the other is impact - sound insulation, also known as structure - borne - sound insulation.
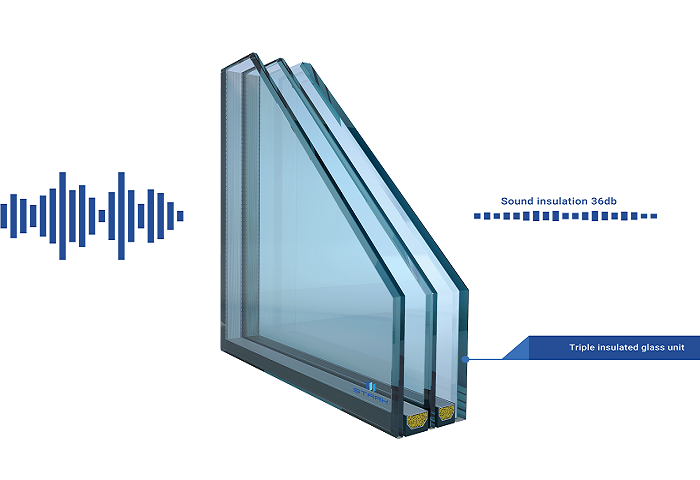
(1) Airborne - sound insulation
Noise that spreads through the air is generally called airborne sound, such as aircraft noise, car horn sound and people's singing, etc.
Using walls, doors, windows or barriers to isolate sounds that spread in the air is called airborne - sound insulation.
(2) Impact - sound insulation
The noise generated and propagated through the structure due to mechanical vibration in a building, such as the sound of footsteps walking on the floor, the dragging sound of tables and chairs, children jumping, and the collision sound when opening and closing doors and windows, etc., is called impact sound, also known as structure - borne sound or solid - borne sound.
Using elastic damping materials for vibration isolation or vibration reduction methods to isolate the impact noise propagated in the structure is called impact - sound insulation.










